AMERISKIN ® Dermatology
www.ameriskin.com
"Bringing Personalized Skin Care to the People of America"
| Home | About Us | Melanoma | Squamous Cell Cancer | Basal Cell Cancer | Pre-Cancers |
| Skin Screening | Notification | Consent | Database | Referrals | Links |
PRE-CANCERS OF THE SKIN
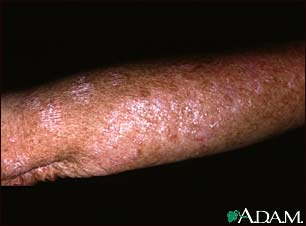
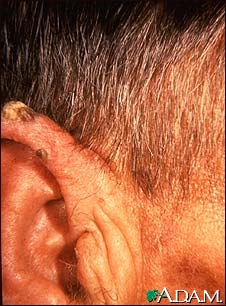
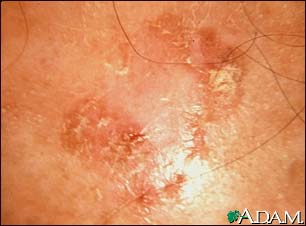
Actinic keratosis
Actinic keratosis is a precancerous skin growth usually caused by sun exposure. Actinic keratosis occurs most commonly in fair skin, especially in the elderly and in young individuals with light complexions. The growths occur in sun-exposed skin areas. The growths begin as flat scaly areas that later develop a hard wart-like surface.
They are classified as precancerous growths. If left untreated, approximately 10% of actinic keratoses develop into squamous cell carcinoma. The following list gives the characteristics of actinic keratoses:
Rough and dry textured skin lesion
A macule, patch, or growth on the skin
Limited to a discrete area (localized)
Located on the face, scalp, back of the hands, chest or other sun-exposed
areas
Color gray, pink, red (erythematous), or the same color as the skin
Surface is initially flat and scaly, then becomes slightly raised
Surface texture becomes hard and wart-like or gritty, rough, and "sandpapery";
may develop a horn-like texture from overgrowth of skin keratin layer (hyperkeratosis)
Note: The skin lesion may be easier to feel than to see.
AMERISKIN ® Dermatology bases the diagnosis on the appearance of the skin growth. A skin biopsy could reveal signs of cancerous changes, if present.
Because actinic keratoses represent precancerous changes, have them examined promptly, and follow your health care provider's advice for treatment.
Growths may be removed by cryotherapy (freezing), electrical cautery (burning), or surgery. Growths may also be treated with topical medications that cause peeling or skin removal.
By itself, actinic keratosis is benign, but it may develop into skin cancer. Removal of the growth is usually effective.
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if areas of persistent roughness or scaliness develop in sun-exposed skin.
Minimize sun exposure and protect skin from the sun. Wear protective clothing such as hats, long sleeved shirts, long skirts, or pants. Ultraviolet light is most intense midday, so try to avoid exposure during these hours.
Use high-quality sunscreens, preferably with SPF (sun protection factor) ratings of at least 15. Pick a sunscreen that blocks both UBA and UVB light. Apply sunscreen at least half an hour before exposure, and reapply frequently.
Use sunscreen for winter exposure also.
AMERISKIN ® Dermatology is a public-private effort in healthcare services related to educating Americans about proper skin care as well as the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of skin conditions, including skin cancers. If you undergo a skin biopsy, the skin specimen may be sent to AMERISKIN ® Dermatology for processing, evaluation, diagnosis, and inclusion in its database.
For more information about our services or to send skin biopsies to us, contact
AMERISKIN ® Dermatology
Byron L. Barksdale, M.D.
© Copyright, 2003-2023. All rights reserved worldwide.
